What is a Trade Blotter?
A trade blotter is a digital record-keeping system specifically designed for tracking and managing financial transactions.
In the dynamic world of finance, efficient and organized trading is essential for success. One indispensable tool that facilitates this process is the trade blotter.
In this article, we will delve into what a trade blotter is, its applications, and the unique advantages it offers compared to a standard table.
Defining a Trade Blotter
A trade blotter serves as a comprehensive electronic logbook that records all the relevant details of financial transactions conducted by a trader or a trading desk. It includes information such as trade date, security traded, quantity, price, counterparty, and other critical data points. Essentially, it provides a centralized platform for traders and portfolio managers to monitor and analyze their trading activities.
Applications of Trade Blotters
Transaction Record Keeping
The primary purpose of a trade blotter is to maintain a detailed record of every trade executed. This includes both historical and real-time data, allowing traders to quickly review and analyze their trading history.
Risk Management:
Trade blotters play a crucial role in risk management. By providing a consolidated view of all trades, traders can assess their risk exposure across different securities and asset classes. This enables timely decision-making to mitigate potential risks.
Compliance and Reporting:
Financial markets are subject to strict regulatory requirements. Trade blotters facilitate compliance by providing a transparent and auditable record of all transactions. This aids in regulatory reporting, ensuring that traders adhere to industry standards and legal obligations.
Performance Analysis:
Analyzing past trades is essential for improving future performance. Trade blotters allow traders to assess the profitability of their trades, identify successful strategies, and learn from any mistakes made during the trading process.
Example Trade Blotter
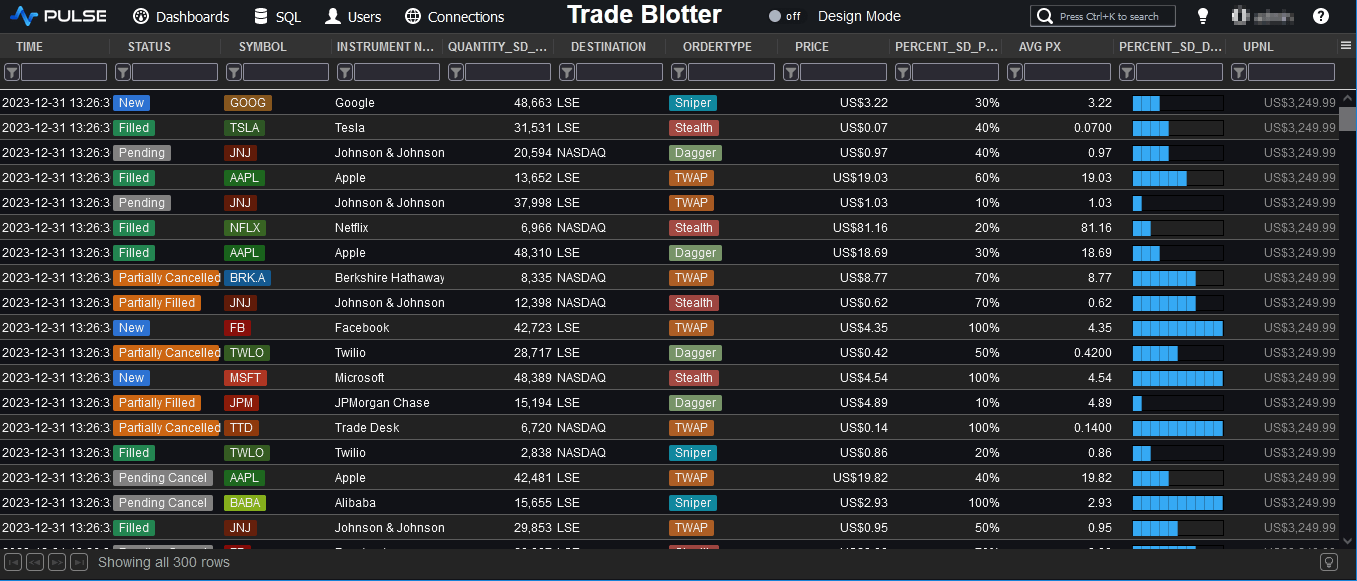
Typical columns in a Trade Blotter
A trade blotter typically includes a range of columns to capture essential information about each financial transaction.
The specific columns may vary depending on the trading platform, the needs of the trading desk, and the type of financial instruments being traded.
However, here are some common columns found in a trade blotter:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Trade Date | Date when the trade was executed. |
| Security | Name or symbol of the financial instrument. |
| Quantity | Number of units or contracts traded. |
| Price | Price at which the trade was executed. |
| Counterparty | Entity or institution on the other side of the trade. |
| Direction | Indicates whether the trade is a buy or a sell. |
| Settlement Date | Date on which the financial transaction is settled. |
| Currency | Currency in which the trade was conducted. |
| Commission/Fees | Transaction costs associated with the trade. |
| Execution Venue | Where the trade was executed (exchange or OTC). |
| Trader ID | Individual or trading desk responsible for the trade. |
| Order ID | Unique identifier assigned to the trade order. |
| Status | Status of the trade (filled, pending, canceled). |
| Strategy/Comments | Notes or comments regarding the trade or strategy. |
| Market Conditions | Information on prevailing market conditions. |
| Risk Metrics | Relevant risk metrics associated with the trade. |
| Trade Type | Type of trade (market order, limit order, stop order). |
| Allocation | How the trade is allocated among different accounts. |
| Tax Lot ID | Identifier for the tax lot associated with the trade. |
| Realized P&L | Realized profit or loss associated with the trade. |
Unique Features of Trade Blotters
Real-Time Updates:
Unlike standard tables, trade blotters provide real-time updates on trading activities. This feature is particularly beneficial in fast-paced financial markets where timely decision-making is critical.
Customization and Filters:
Trade blotters offer a high degree of customization, allowing users to filter and sort data based on specific criteria. Traders can focus on particular securities, time frames, or trading strategies, streamlining the analysis process.
Integration with Market Data:
Trade blotters often integrate seamlessly with market data feeds, providing traders with up-to-the-minute information on market conditions. This integration enhances decision-making by ensuring that traders have the latest relevant data at their fingertips.
Automated Workflows:
Many trade blotters feature automated workflows, reducing manual data entry and the likelihood of errors. Automation improves efficiency and allows traders to allocate more time to strategic decision-making rather than administrative tasks.
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial markets, the adoption of technology is paramount for success.
Trade blotters stand as a testament to this, offering traders and financial professionals a powerful tool for managing, analyzing, and optimizing their trading activities. With their real-time updates, customization options, and integration capabilities, trade blotters provide a powerful tool, empowering users to navigate the complexities of financial markets with confidence.