What is a Time-Series Database
What is a time-series Database?
Who uses them? Why? What for?
Time-Series Database -> A database with a specialized structure to allow efficiently storing and analysing time-series.
Time-Series -> A series of data points with associated timestamps.
Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data.
Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Contents
The Time-Series Problem
Typically users that have a time-series problem:
- Have 1000s of events occurring at timestamps
- They want to record every single event with highly accurate time-stamps
- They have Big Data because even one value measured over time can create a lot of data
- For analysis they want to be able to:
- Perform aggregate queries on date/time buckets
- Perform time-window functions within the time-buckets e.g. Find first/last/max/min within a time window
- Perform Time-Joins. For example if you have an event X at time T0, what is the closest event in time from table Y.
- Since older data is less valuable we would like to archive it to save on storage
Example Time-Series Queries
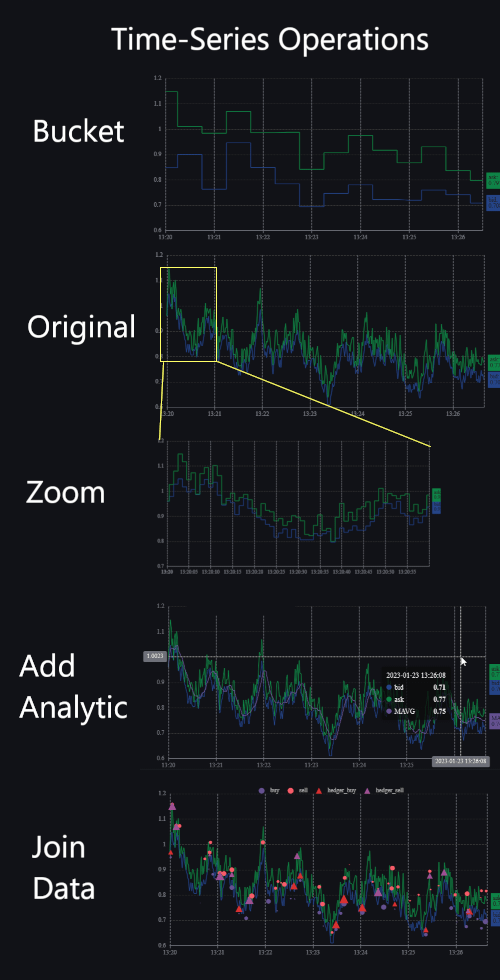
Time-Series Database Features
Increasingly businesses are realizing a one size fits all isn't working for databases. When you want to perform certain time based analyses, time-series databases can provide a 100x speedup.
A time-series database is specialized to quickly and efficiently:
- Selecting a Time-Range
- Answer queries requiring Time-Joins - e.g. Event X occurred at 9am, when was the closest Y event to that.
- To provide elegant Date/Time-Functions - specialized functions to allow handling date/time types well. e.g. bucketing, range querying
- Allow Compression - As the data is large and often repeating
- Support Nanoseconds - As for some industries e.g. trading, the exact timing of events matter.
Why are time-series databases important now?
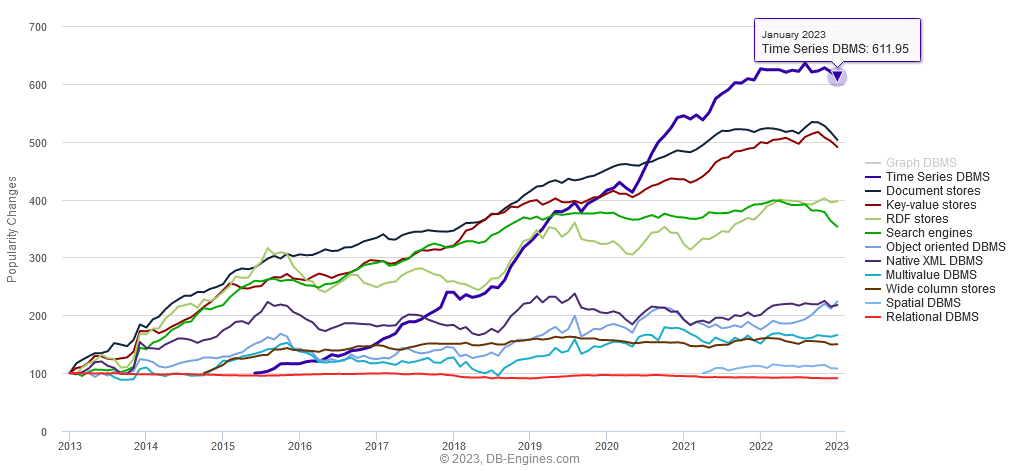
In the past machines, storage and technology would have made storing the full stream of time values too costly. However with plummeting compute/storage costs storing every single user click or stock price movement began to make sense. That has now led to renewed investment in time-series databases to expand their audience. As you can see below the number of time-series databases available has exploded:
Fastest Growing Database Segment
Who uses time-series databases?
| User | Product | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Banks - barclays, DB, Citi, UBS, HSBC, bank of America | kdb | To store tick data - fine-grained stock/FX price movements. |
| User Analytics | Google Analytics, Baidu - Doris, Yandex - Clickhouse | Used to clicker website visitor metrics |
| IoT - Internet of Things | InfluxDB | Gathering metrics from 1000 of deployed devices and performing problem identification or aggregation queries. |
| Monitoring | Prometheus/Grafana | Gathering metrics from 1000 of deployed software services and logs. |
Top Time-Series Databases
Next read our list of Top Time-Series Databases